The emergence of Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) is one of the most significant cybersecurity challenges that businesses currently face. Forbes estimates that by 2025, global cybercrime damages will amount to $10.5 trillion annually, highlighting the substantial financial impact of sophisticated attacks such as Advanced Persistent Threats. These threats entail protracted, covert campaigns in which hackers infiltrate networks and remain undetected for months or even years, covertly stealing confidential information or disrupting critical business processes. The complexity and risk posed by APTs continue to increase quickly as businesses spread their digital footprints across distributed networks and cloud environments.
At this point, it is worthwhile to consider the wisdom of cybersecurity pioneer Kevin Mitnick, a top security consultant and one of the most infamous hackers in history. “The human element is the weakest link in security,” he famously stated. This result highlights why APTs frequently employ social engineering techniques to gain initial access by exploiting human weaknesses. Designing effective defenses that go beyond technology alone requires an understanding of this human factor.
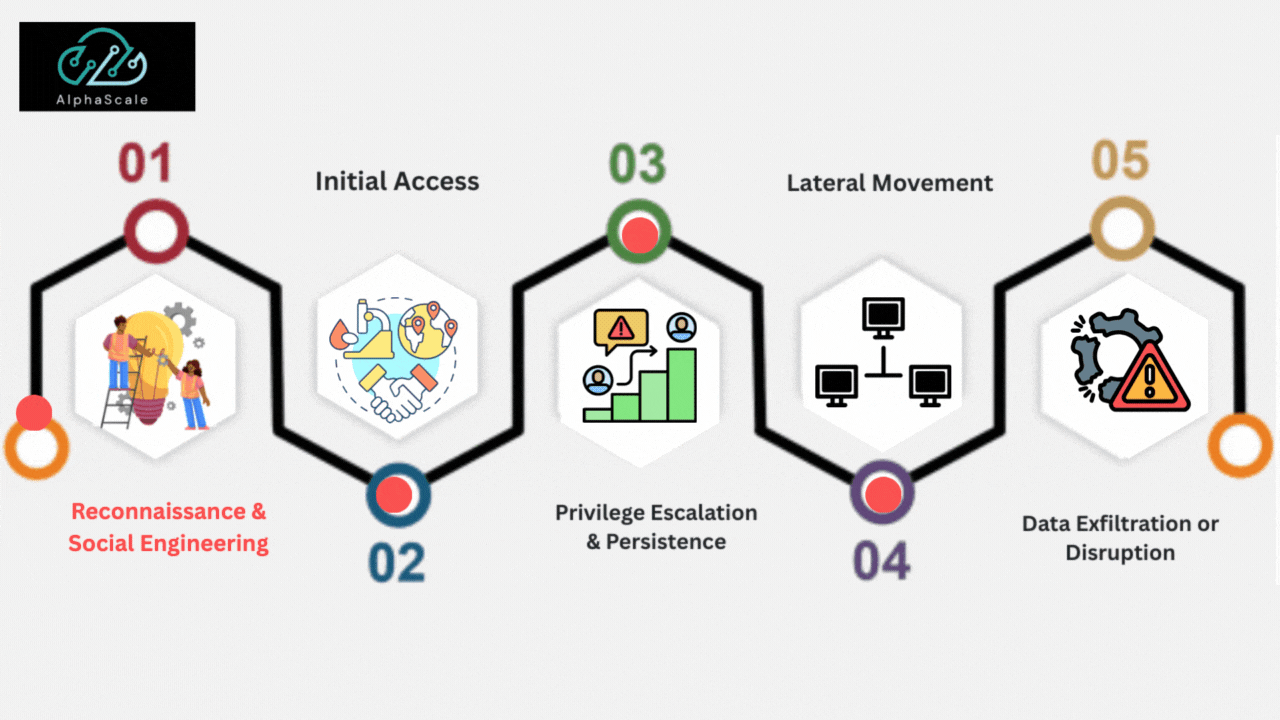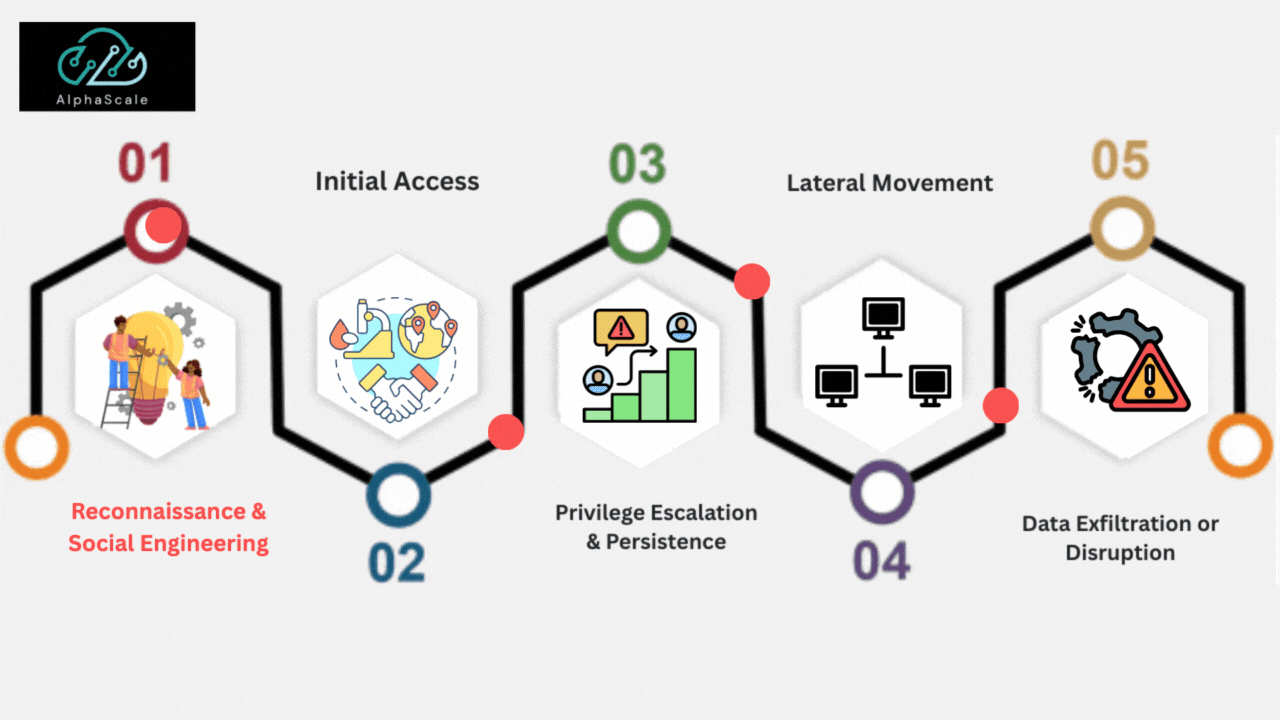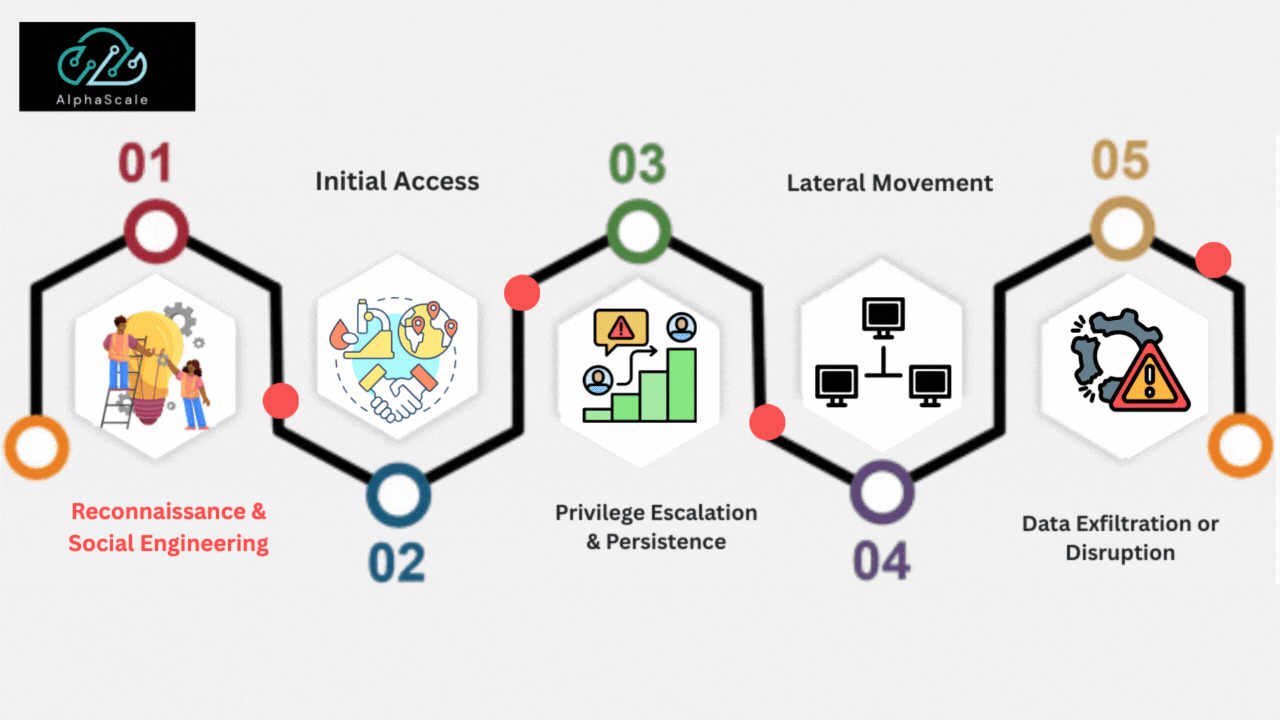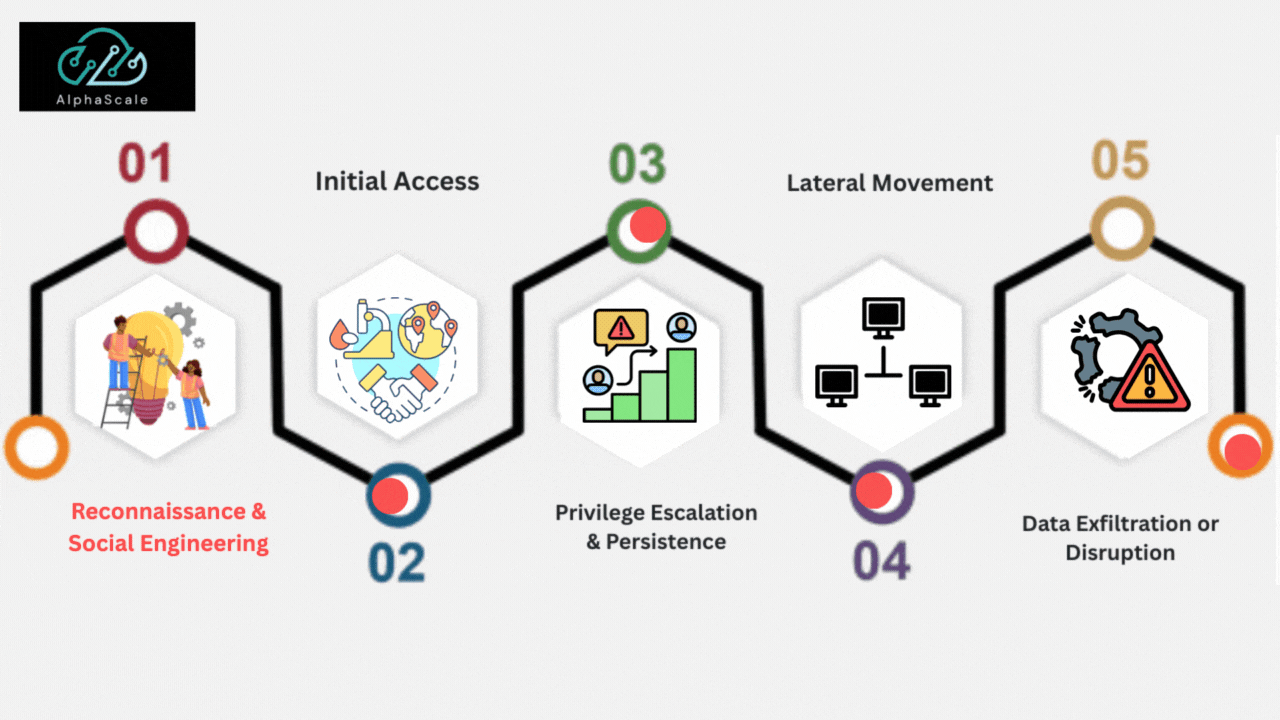
The increasing frequency of sophisticated cyberattacks necessitates a fundamental change in how businesses protect themselves. When it comes to adversaries who continually adapt and refine their strategies, traditional security measures are no longer sufficient. Organizations must implement a multi-layered defense strategy that incorporates real-time threat intelligence, continuous monitoring driven by artificial intelligence, and zero-trust principles. APTs require robust security defenses, including advanced monitoring, threat detection, and swift incident response capabilities, due to their clandestine nature. Businesses can significantly reduce attackers’ window of opportunity by adopting these cutting-edge strategies, ensuring that threats are identified and eliminated before permanent damage is done.
Let’s Understand APT Attacks
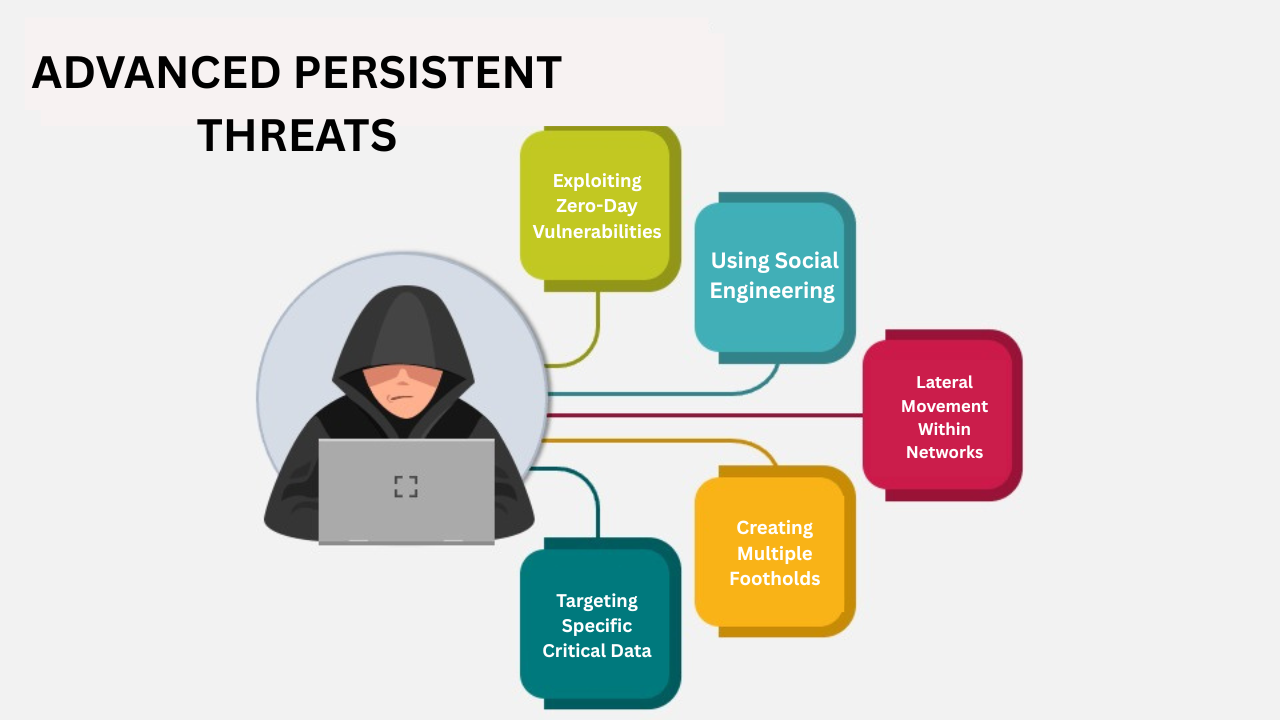
The multi-stage process used by Advanced Persistent Threats is meticulously planned. Attackers frequently employ social engineering techniques, such as phishing or exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities, to gain initial access. After entering the network, they laterally traverse the divided environments, increasing their level of privilege and creating multiple footholds to evade detection.
APTs are especially difficult to detect and eliminate with conventional security tools, such as firewalls or signature-based antivirus programs, due to their complex infiltration techniques. Organizations require dynamic and adaptable defense systems that can respond instantly to evolving threats and counter these advanced strategies. By utilizing AI-driven SIEM and SOAR automation to reduce inaccurate results and deliver actionable intelligence for prompt responses, platforms like AlphaScale enhance this defense. Since APTs are frequently linked to nation-state actors, these cyber threats are typically well-funded and carefully planned, making them difficult to identify and counter.
Why network segmentation and zero trust matter
Adopting a Zero Trust security model, which requires rigorous authentication and ongoing validation of each user, device, and application trying to access network resources, is the first step in a strong defense against APTs. Even if attackers can get past the initial points of entry, this strategy severely restricts their freedom of movement within the network.
Network segmentation, which limits lateral movement and shields sensitive data and systems from prevalent compromise, is a complementary strategy to Zero Trust. The unified platform from AlphaScale facilitates the smooth integration of these tactics, allowing businesses to effectively implement segmentation policies and extensive access controls, improving their overall security posture.
Using AI and threat intelligence
Identifying the subtle signs of APT activity requires continuous observation and attention. To analyze large amounts of network data and identify anomalies that may indicate a breach, artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are crucial. This is enhanced by Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) and Advanced Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), which provide automated responses to suspicious activity and real-time alerts. These capabilities are further enhanced by AlphaScale’s Gen-AI-powered threat intelligence platform, which offers proactive recommendations and real-time insights, enabling security teams to mitigate risks before they escalate into serious incidents.
Raising user awareness and managing risks
An essential component of APT defense is efficient vulnerability management. Timely updates and automated patching eliminate security flaws that hackers commonly use to access networks. Furthermore, by limiting network communication to trusted domains and approved software and allowing only approved applications, domain allowlisting reduces the likelihood of encountering malicious payloads. By identifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities, integrating current threat intelligence feeds helps organizations stay ahead of new attack vectors.
Since social engineering remains a significant attack vector for APTs, raising cybersecurity awareness among staff members is equally crucial. Regular training significantly reduces the likelihood of successful infiltration by enabling users to identify and report suspicious activity. The AlphaScale platform supports these initiatives by providing real-time recommendations and contextual vulnerability analysis, allowing businesses to maintain a proactive and secure posture.
Staying Secure Against APTs
Businesses will be significantly less vulnerable to Advanced Persistent Threats by 2025 if they apply multi-layered defense strategies that combine AI-driven monitoring, zero trust, and real-time threat intelligence. By encouraging organizations to respond proactively and streamline security operations, platforms such as AlphaScale transform complex cyber challenges into feasible risks.
